Table of Content
Because of this, the PSA test on its own is not recommended as a screening test for prostate cancer. But men over 50 can usually ask their GP for a PSA blood test if they want. Your GP will explain the potential benefits and risks of having a PSA test. Overall research has shown that current tests don’t reduce the number of men dying from prostate cancer. Or see if the current test is more effective if used in a different way and can find the cancers that need treatment more accurately.
As with most cancers, survival for prostate cancer is improving. The detection of a greater proportion of latent, earlier, slow-growing tumours in more recent time periods will have the effect of raising survival rates due to lead-time bias . Lead-time bias for prostate cancer is estimated to be between five and 12 years, varying with a man's age at screening.
From Mayo Clinic to your inbox
Patients around the globe have access to incredible amounts of medical resources. If you have an increased risk of getting prostate cancer. If any polyps are found during the test, the doctor may remove them with a small instrument passed through the scope. If a pre-cancerous polyp or colorectal cancer is found, you’ll need to have a colonoscopy later to look for polyps or cancer in the rest of the colon. In the UK, they now use the Cambridge Prognostic Group system that divides prostate cancer into 5 risk groups.
Talk to your GP if you're worried about prostate cancer. Or if you have urinary symptoms such as difficulty passing urine. The risk of prostate cancer also increases as men get older. It’s a protein made by both normal and cancerous prostate cells. It's normal for all men to have some PSA in their blood. The UK National Screening Committee doesn’t currently recommend screening for prostate cancer.
Statistics by cancer type
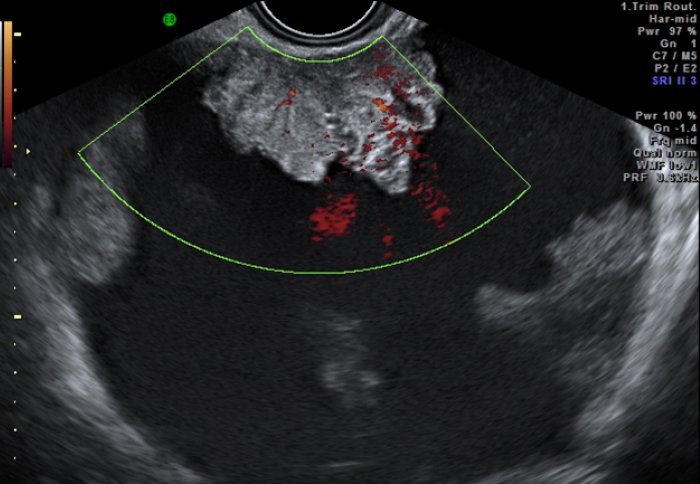
Every year, around 52,000 men will be diagnosed with the disease. However, while prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men, it is very difficult to spot early because it doesn’t cause symptoms in its early stages. Keith Law, a 71-year-old from East Sussex, shares his journey with the disease. Digital rectal examination is when a health care provider inserts a gloved, lubricated finger into a man’s rectum to feel the prostate for anything abnormal, such as cancer. The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force does not recommend DRE as a screening test because of lack evidence on the benefits.
The goal of screening for prostate cancer is to find cancers that may be at high risk for spreading if not treated, and to find them early before they spread. But most prostate cancers grow slowly and don’t cause any health problems. If a screening test finds a slow-growing cancer, it may cause you to worry, and lead to unneeded tests and treatments that can have serious side effects.
Funding research that will stop men dying from prostate cancer
Talk to your healthcare provider to see if the prostate-specific antigen test is right for you. The information on this page is based on literature searches and specialist checking. We used many references and there are too many to list here. Please details of the particular issue you are interested in if you need additional references for this information. The screening programme should also be good value for money for the NHS. We know it’s a worrying time for people with cancer, we have information to help.

Data from the European Randomized Study of Prostate Cancer estimates that for a single screening test, mean lead times are 12 years at age 55 and six years at age 75. Some of the increase may also be attributed to genuine improvements in survival due to more effective treatment, for both early, aggressive prostate cancers and advanced cases. But if your hospital doesn’t do this type of surgery, your doctor may be able to refer you to one that does. Balloons may be an option if you still leak urine more than six months after your prostate cancer treatment. But you probably won’t be able to have them if you’ve had radiotherapy. While there is no clear reason for these differences, several factors can impact cancer risk and outcomes in the African American community.
The content on this site is intended for healthcare professionals. In cases where cancer has been confirmed, you should not have to wait more than 31 days from the decision to treat to the start of treatment. But in many cases your symptoms will not be related to cancer and will be caused by other, non-cancerous health conditions. Cancer sometimes begins in one part of the body before spreading to other areas. Influenza, or the flu, is caused by one of several types of viruses that can spread quickly from person to person via airborne particles. The colon and rectum should be emptied before this test to get the best pictures.
A man’s prostate-specific antigen blood level is often a good indicator of how effective treatment is or has been. Generally speaking, your PSA level should get very low after treatment. But PSA results aren’t always reliable, and sometimes doctors aren’t sure what they mean. Yearly PSA testing in men without symptoms is generally not recommended. However, in men who report prostate symptoms, PSA testing can help doctors determine the nature of the problem. In men who have been treated for prostate cancer, the PSA test may be used to see if the cancer has come back.
Some evidence shows that faster-rising PSA levels may be a sign of cancer. Men who have a PSA level that doubles within a 3-month period tend to have a worse prognosis compared to men whose PSA level does not double. If you choose observation or active surveillance, your PSA level will be monitored closely to help decide if the cancer is growing and if treatment should be considered. Before starting treatment, you might want to ask your doctor what your PSA level is expected to be during and after treatment, and what levels might cause concern.
An estimated 280,500 men who had been diagnosed with prostate cancer between 1991 and 2010 were alive in the UK at the end of 2010. Prostate cancer incidence rates are projected to rise by 12% in the UK between 2014 and 2035, to 233 cases per 100,000 males by 2035. In the more traditional approach to prostatectomy, called an open prostatectomy, the surgeon operates through a single long skin incision to remove the prostate and nearby tissues. This type of surgery is done less often than in the past. Prostate cancer is the most commonly diagnosed cancer among Canadian men. Talk to your doctor about how to detect prostate cancer early.
Treatment for prostate cancer depends on whether cancer is in part or all of the prostate, or if it has spread to other parts of the body. Talk with your doctor about the best treatment choice for you and the possible side effects of treatment. You may want to ask another doctor for a second opinion.
It’s put in through the anus and into the rectum and colon. Special instruments can be passed through the colonoscope to biopsy or remove any suspicious-looking areas such as polyps, if needed. The fecal immunochemical test checks for hidden blood in the stool from the lower intestines.